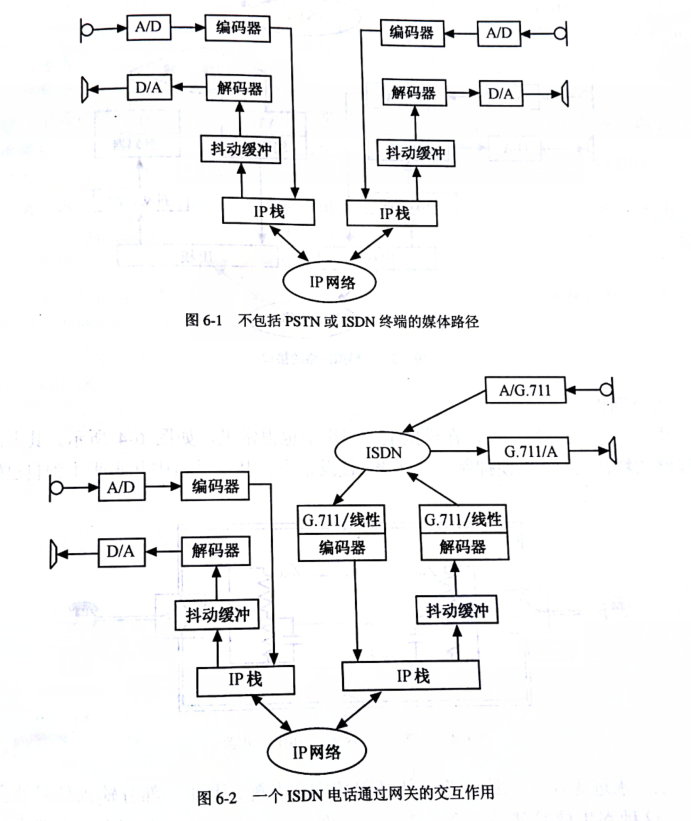
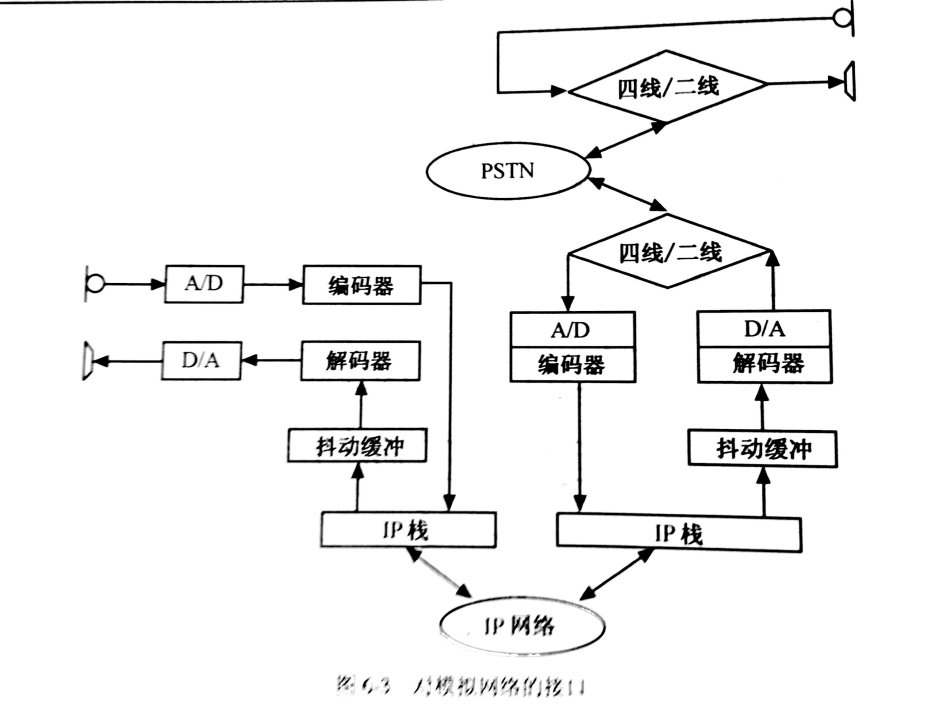
Compared to traditional conference call bridges, controlling echo and delay when carrying voice over IP networks is a key technology for Voip. The media path for an IP phone call can be represented by Figure 6-1, which does not include the PSTN or ISDN terminals. When an ISDN phone interacts through the gateway, the situation is slightly duplicated, as shown in Figure 6-2. When the gateway interface is connected to an analog network, the user-to-network interface requires only two lines (input and output signals share a pair of lines) in most cases. In this case, a four-wire/second-line hybrid circuit is required, as shown in Figure 6-3. Show. In the VOIP system, the factors causing the deterioration of voice quality are:
(1) IP network packet loss, delay and jitter. This can cause a reduction in the sound quality of the conference call. (2) End-to-end delay and frame loss caused by the jitter buffer. It will cause a large delay in the conference call.
(3) Acoustic echo caused by sound interface. Echo is also an important assessment indicator for the conference call system.
The relevant content of the voice network quality control technology in the telephone network is completely described in the ITU Recommendations. The discussion here mainly focuses on the impact on the end user's feelings in voice quality. In most cases, the traditional circuit switched telephone and the current IP telephone are mostly the same. . However, IP telephony networks have special factors such as long delays, jitter, and loss. Therefore, a new framework is needed to assess voice quality. This work is being studied in ESTITIPHON (Working Group 5).
1. Echo in the telephone network 2. The most important echo in the telephone network is the echo of the call—it is the delayed own voice channel that the caller has channeled. Various echoes are caused by the recipient's electrical echo or acoustic echo. If the echo of the caller is reflected in 2 words, he will also affect the receiver. This is where the callee hears the voice of two callers - first a large signal, then a weak signal that is delayed for a long time. This is the echo of the receiver.
(1) Hybrid echo mixing circuits are used for 2/4 wire conversion and are also common in analog conference call bridges, as shown in Figure 6-4. Among them, Zref is used to match the characteristic impedance of the telephone conference line in order to suppress the echo of the speech, so that the talker is hardly hearing his voice in his receiver.
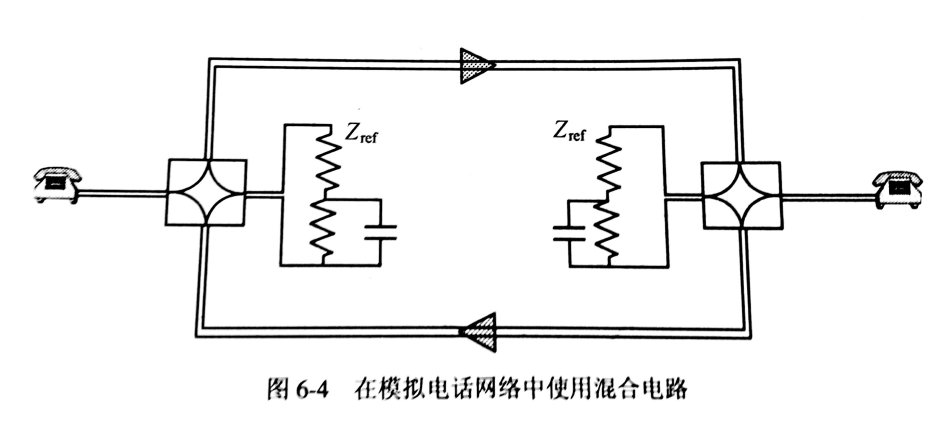
In fact, the characteristic impedance of a two-wire line can never be exactly matched, so a part of the input signal will be fed back to the output signal. This spurious signal is mixed echo. On the one hand, it will cause the signal to cycle between the two amplifiers. If the delay is about 20ms, it will cause a "church effect." In order to avoid the instability of the network, it is at least 6 dB to reduce the signal of the four-wire path. On the other hand, the Zref mismatched conference call will feed back all input signals on the network, and the other party's caller will hear her own voice after a round trip time.
In many countries, the transmission network consists entirely of four-wire lines. The two-wire and four-wire conversions only occur where the local exchange links analog telephones. There is no delay because the switch echoes back to the phone, so there is no impact. On the other hand, the echo generated at one end of the telephone is immediately noticed through the network back to the other end, and the round-trip time is about 50 ms.
(1) Acoustic echo Acoustic echo refers to the feedback of part of the sound signal to the same side of the receiver. The common “hands-free phone†is a kind of amplified phone with acoustic echo cancellation, and the “conference phone†is a kind of amplified phone without acoustic echo cancellation. The common conference phones include Polycom's extended, standard, soundstation2, Octopus conference phone, Meeteasy, Konftel, and sound network.
A typical acoustic echo is a spurious signal of about 10-15 dB or less compared to a person speaking with a microphone or using a conference call coupler device, similar to a hybrid echo. This multiple of acoustic echo will not cause people's attention if its delay is below 29ms; if it is 40ms, the conference room at the other end of the line will sound like the other party is talking in the well; if the round trip time exceeds 40ms, the situation will be worse.
A simple way to suppress acoustic noise is to use a headset, but if you use appropriate equipment, the power of the parasitic echo can be controlled to less than 45 dB of the talker signal, even with a speakerphone. ITU Recommendation G.168 gives some recommended indicators for typical echo path testing.
Echo cancellers usually cannot eliminate acoustic echoes and electrical echoes at the same time because the path of acoustic echoes varies widely, so it is difficult to find a dynamic adaptation to the synthesized echo. For ITU's special echo cancellers, the performance of G.168 may not be enough. The new word has a new suggestion that G.168 has taken effect, and some have already been implemented by some manufacturers. This suggestion includes some useful content, such as the ability to stop echo cancellation when a high-speed modem's phase-reversal tone is detected. The typical attenuation values ​​for acoustic echo in current teleconference devices are: 10-15 dB for speakerphones; 35-40 dB for hands-free or high quality handsets. The conference call coupler, the audio processor can well eliminate the echo and howling of the conference call, ensuring the clarity of the voice quality of the conference call. The system is stable.
(1) IP network packet loss, delay and jitter. This can cause a reduction in the sound quality of the conference call. (2) End-to-end delay and frame loss caused by the jitter buffer. It will cause a large delay in the conference call.
(3) Acoustic echo caused by sound interface. Echo is also an important assessment indicator for the conference call system.

The relevant content of the voice network quality control technology in the telephone network is completely described in the ITU Recommendations. The discussion here mainly focuses on the impact on the end user's feelings in voice quality. In most cases, the traditional circuit switched telephone and the current IP telephone are mostly the same. . However, IP telephony networks have special factors such as long delays, jitter, and loss. Therefore, a new framework is needed to assess voice quality. This work is being studied in ESTITIPHON (Working Group 5).
1. Echo in the telephone network 2. The most important echo in the telephone network is the echo of the call—it is the delayed own voice channel that the caller has channeled. Various echoes are caused by the recipient's electrical echo or acoustic echo. If the echo of the caller is reflected in 2 words, he will also affect the receiver. This is where the callee hears the voice of two callers - first a large signal, then a weak signal that is delayed for a long time. This is the echo of the receiver.

(1) Hybrid echo mixing circuits are used for 2/4 wire conversion and are also common in analog conference call bridges, as shown in Figure 6-4. Among them, Zref is used to match the characteristic impedance of the telephone conference line in order to suppress the echo of the speech, so that the talker is hardly hearing his voice in his receiver.

In fact, the characteristic impedance of a two-wire line can never be exactly matched, so a part of the input signal will be fed back to the output signal. This spurious signal is mixed echo. On the one hand, it will cause the signal to cycle between the two amplifiers. If the delay is about 20ms, it will cause a "church effect." In order to avoid the instability of the network, it is at least 6 dB to reduce the signal of the four-wire path. On the other hand, the Zref mismatched conference call will feed back all input signals on the network, and the other party's caller will hear her own voice after a round trip time.
In many countries, the transmission network consists entirely of four-wire lines. The two-wire and four-wire conversions only occur where the local exchange links analog telephones. There is no delay because the switch echoes back to the phone, so there is no impact. On the other hand, the echo generated at one end of the telephone is immediately noticed through the network back to the other end, and the round-trip time is about 50 ms.
(1) Acoustic echo Acoustic echo refers to the feedback of part of the sound signal to the same side of the receiver. The common “hands-free phone†is a kind of amplified phone with acoustic echo cancellation, and the “conference phone†is a kind of amplified phone without acoustic echo cancellation. The common conference phones include Polycom's extended, standard, soundstation2, Octopus conference phone, Meeteasy, Konftel, and sound network.
A typical acoustic echo is a spurious signal of about 10-15 dB or less compared to a person speaking with a microphone or using a conference call coupler device, similar to a hybrid echo. This multiple of acoustic echo will not cause people's attention if its delay is below 29ms; if it is 40ms, the conference room at the other end of the line will sound like the other party is talking in the well; if the round trip time exceeds 40ms, the situation will be worse.
A simple way to suppress acoustic noise is to use a headset, but if you use appropriate equipment, the power of the parasitic echo can be controlled to less than 45 dB of the talker signal, even with a speakerphone. ITU Recommendation G.168 gives some recommended indicators for typical echo path testing.
Echo cancellers usually cannot eliminate acoustic echoes and electrical echoes at the same time because the path of acoustic echoes varies widely, so it is difficult to find a dynamic adaptation to the synthesized echo. For ITU's special echo cancellers, the performance of G.168 may not be enough. The new word has a new suggestion that G.168 has taken effect, and some have already been implemented by some manufacturers. This suggestion includes some useful content, such as the ability to stop echo cancellation when a high-speed modem's phase-reversal tone is detected. The typical attenuation values ​​for acoustic echo in current teleconference devices are: 10-15 dB for speakerphones; 35-40 dB for hands-free or high quality handsets. The conference call coupler, the audio processor can well eliminate the echo and howling of the conference call, ensuring the clarity of the voice quality of the conference call. The system is stable.
Storage bins are containers used to organize, store, and transport items. They come in a variety of sizes, shapes, materials, and designs, depending on their intended use. Common types of storage boxes are plastic boxes
Storage boxes can be used in a variety of environments, including homes, offices, warehouses and retail stores. They are especially useful for organizing and maximizing space, as they keep items neatly stacked and easily accessible.
In homes, storage boxes are often used to store seasonal items, clothes, books, toys, and other household items. In offices, they can be used to organize documents, stationery and office supplies. In warehouses and retail stores, large storage bins are used to store and transport goods.
Storage boxes can also come with additional features such as lids, handles, wheels or compartments for added convenience and functionality. Some storage boxes are also designed to be decorative and double as stylish home accents.Storage Boxes,Storage Bins,Plastic Box,Plastic Storage Bins
Kunshan Muchun Electric Co., LTD , https://www.nbmuchunelectric.com