Carbon-based materials are regarded as the most promising negative electrode materials for sodium ion batteries due to their abundant resources, low price and environmental friendliness. Hard carbon, carbon black, carbon fiber and graphene have been reported in succession. Unfortunately, most carbon materials have the first problem of low coulombic efficiency and poor cycle performance to varying degrees, and the doping of heteroatoms (such as B, N, S, P) can improve the above problem because it can improve Conductivity, while at the same time introducing an active site that binds to sodium ions, nitrogen-doped carbon-based materials have been extensively studied and have shown significant advances as sodium negative electrodes.
Compared with nitrogen, sulfur has a larger atomic size and less electronegativity. It is more favorable for increasing the interlayer spacing, introducing active sites, and enhancing the electrical properties of carbon-based materials. From the perspective of the synergistic effect of two-element doping, N/S co-doping is an effective way to achieve high conductivity and widen layer spacing. However, sulfur-containing precursors are often used as a source of sulfur, and sodium intercalation can only be increased by increasing the interlayer spacing, and an additional Faraday reaction cannot be provided to further increase the sodium storage capacity.
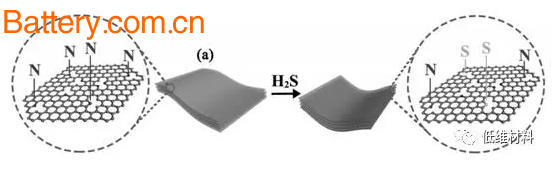
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of sulfur doping
In order to solve such problems, the team of Professor Zhou Zhen of Nankai University adopted a completely different way of sulfur doping - heat treatment of nitrogen-rich carbon nanosheets under H2S atmosphere.
This method directly replaces pyrrole N with S by gas-solid reaction, and improves the utilization of S by forming a -CSC- bond (as shown in Figure 1), while increasing the interlayer spacing (Fig. 2) provides more The active site satisfies a highly reversible sodium storage reaction, and thus the nitrogen-sulfur co-doped porous carbon nanosheet (SN/C) exhibits high capacity and excellent rate performance when used as a sodium negative electrode.
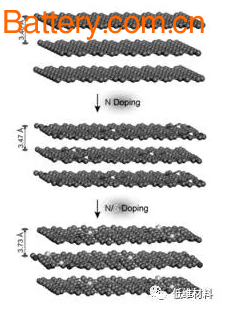
Fig. 2 Effect of nitrogen-sulfur doping on the spacing of carbon material layers
It can be seen from the CV of SN/C that compared with N/C, SN/C has a reduction peak at 1.05V, corresponding to the reaction between Na+ and S bonded to the carbon substrate, and has an oxidation at 1.8V. The peak indicates that the partial capacity of SN/C is contributed by the Faraday reaction between Na+ and S. At a current density of 50 mA/g, the stable capacity can be maintained at about 350 mAh/g, and even if the current density is increased to 10 A/g, the capacity can be maintained at about 110 mAh/g, exhibiting excellent rate performance.
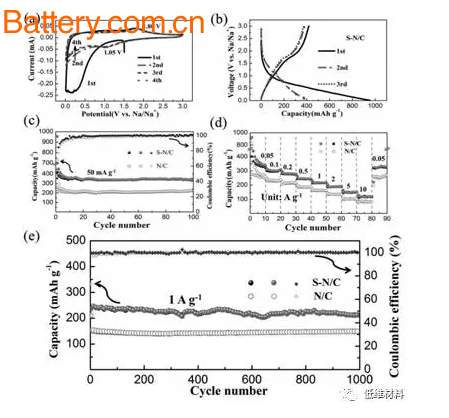
Figure 3 SN/C electrochemical performance
Binding Wire is made from high quality low carbon steel Q195 and Q235, through the process of drawing, annealing, acid washing and galvanizing. The wire diameter ranges from 0.5mm to 5.0mm, usually goes in 0.5kg-1000kg per coil.It has a bright surface and a good corrosion resistance, widely used in agriculture, building, construction and wire mesh industries.



Galvanized Wire,Galvanized Wire Mesh,Galvanized Steel Wire,Galvanised Steel Mesh
Shenzhou City Shengsen Metal Products Co., Ltd. , https://www.xsswiremesh.com